The exploration of profound philosophical concepts spans across diverse traditions, from ancient spiritual practices to modern scientific theories. In this paper, we delve into the intriguing parallels between Vajrayana Buddhism’s Four Immeasurables and quantum theory’s concept of super symmetry dualism.
By examining these seemingly disparate frameworks, we aim to uncover common threads that illuminate the nature of reality and consciousness.
Vajrayana Buddhism and the Four Immeasurables:
Vajrayana Buddhism, a wisdom tradition, emphasizes the cultivation of compassion and wisdom as a path to enlightenment. Central to Vajrayana practice are the Four Immeasurables.
These are:
1. Loving-kindness (Metta): The wish for all beings to experience happiness and well-being.
2. Compassion (Karuna): The empathetic desire to alleviate the suffering of others.
3. Sympathetic joy (Mudita): Rejoicing in the happiness and success of others.
4. Equanimity (Upekkha): Maintaining a balanced and non-reactive mind in the face of both joy and suffering.
These Four Immeasurables form the foundation of Vajrayana ethical conduct and meditation practices, fostering the development of boundless love, compassion, joy, and equanimity towards all beings.
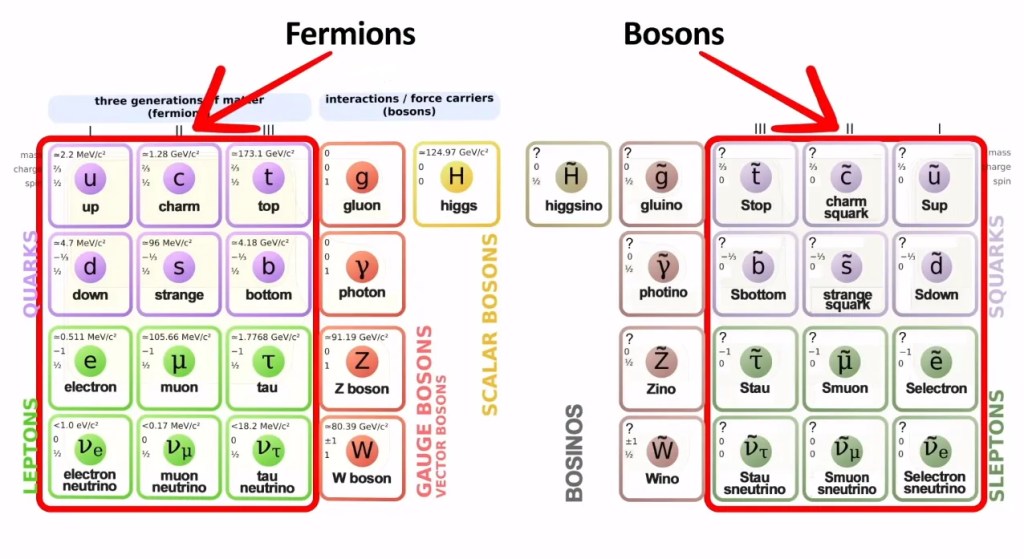
In quantum theory, super symmetry is a proposed fundamental symmetry between elementary particles and their corresponding superpartners. Super symmetry posits that for every known particle, there exists a superpartner particle with similar properties but differing by half a unit of spin. This symmetry suggests a deep underlying unity in the fabric of reality, transcending the apparent duality between matter and energy.
The concept of super symmetry dualism in quantum theory challenges conventional notions of materialism and underscores the interconnectedness of all phenomena at the quantum level. Just as Vajrayana Buddhism teaches the interdependence of all beings and phenomena, super symmetry dualism suggests a profound unity underlying the diversity of the universe.
When we account for their apparent differences in language and methodology, Vajrayana Buddhism’s Four Immeasurables and quantum theory’s super symmetry dualism share several intriguing parallels:
1. Unity and Interconnectedness: Both frameworks emphasize the fundamental unity and interconnectedness of all phenomena, transcending conventional distinctions between self and other, particle and wave.
2. Boundless Compassion: The cultivation of boundless love and compassion towards all beings in Vajrayana Buddhism resonates with the inclusive nature of super symmetry dualism, which acknowledges the inherent value and interconnectedness of all particles and fields.
3. Equanimity and Balance: Just as equanimity in Vajrayana Buddhism promotes a balanced and non-reactive mind, super symmetry dualism suggests a dynamic equilibrium underlying the fluctuations of the quantum world.
In exploring the parallels between Vajrayana Buddhism’s Four Immeasurables and quantum theory’s super symmetry dualism, we gain insight into the profound interconnectedness of consciousness and the cosmos. Both frameworks offer valuable perspectives on the nature of reality, challenging us to transcend dualistic thinking and cultivate compassion, wisdom, and equanimity in our lives. As we continue to probe the mysteries of existence, may these diverse paths of inquiry converge, illuminating the path to deeper understanding and harmony.
QP




